2.1 rocket_client lib - Connecting to a Rocket Editor
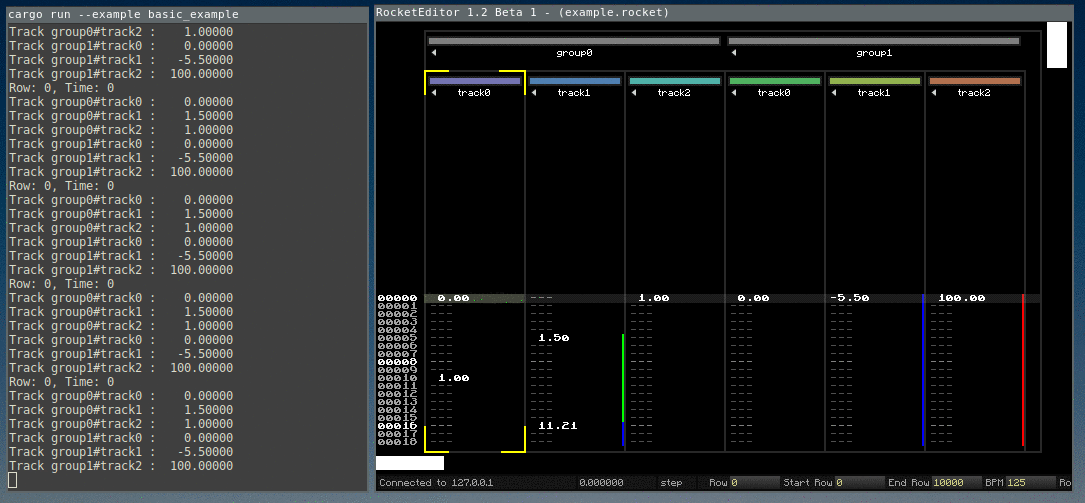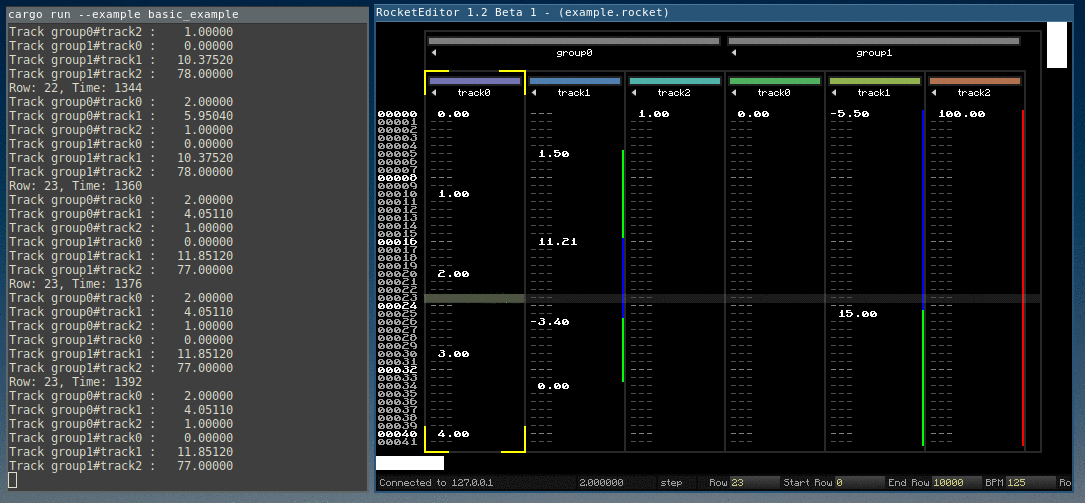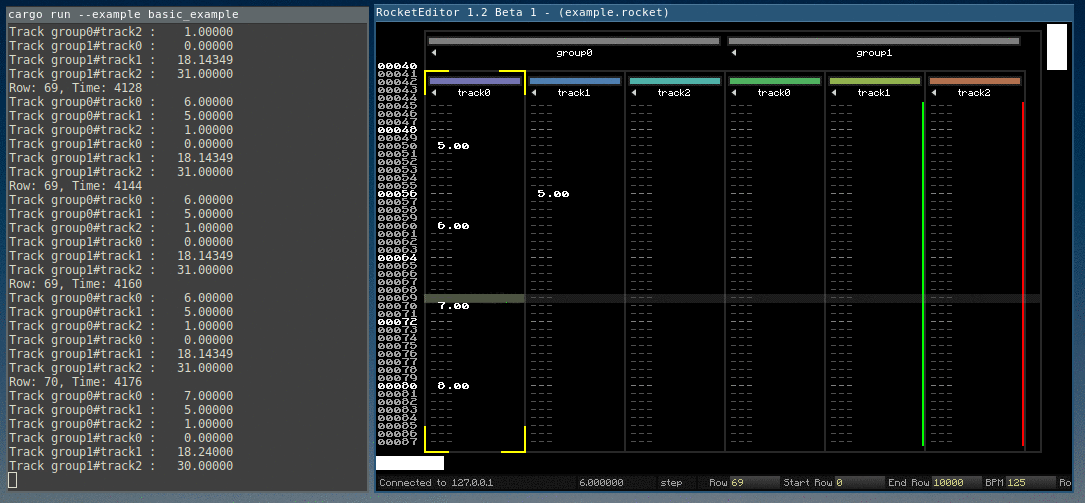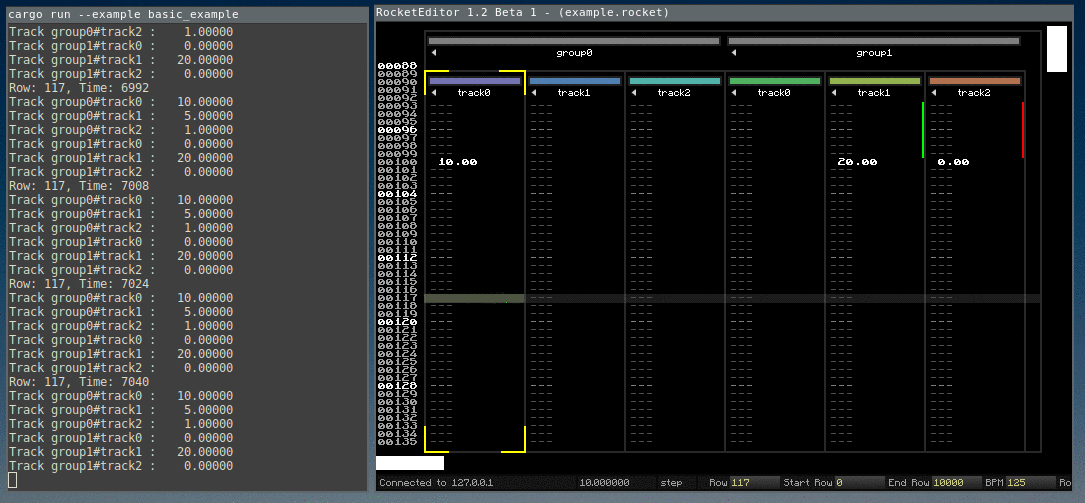
A minimal example is included as basic_example.rs.
Summary
Rocket listens on localhost:1338. When we connect, a handshake is completed.
After this we listen to instruction bytes or send them to the editor.
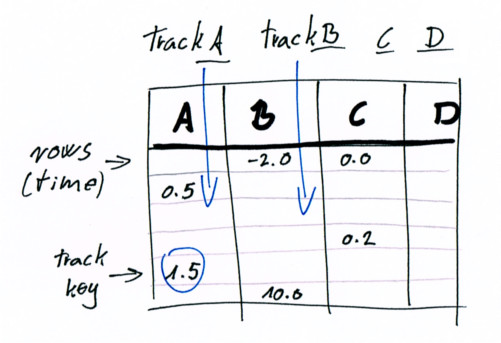
For example, when the user edits a value in the editor, Rocket sends a message describing the track index, row and value of the key, and the interpolation type.
Then the demo tool has to update its own data, inserting a key value in a track in this case.
The interpolated values are calculated by the rocket_sync lib (overview in the next chapter).
Code Overview
The client is ~300 lines sloc, follow along with the code in lib.rs.
The SyncClient struct wraps a TcpStream which we use to send and receive bytes from Rocket.
The instruction bytes are represented by SyncCmd.
pub struct SyncClient {
stream: TcpStream,
}
pub enum SyncCmd {
SetKey,
DeleteKey,
GetTrack,
SetRow,
Pause,
SaveTracks,
NOOP,
}
/// Connects to the Rocket Editor server and shakes hand with it
pub fn new(address: &str) -> Result<SyncClient, Box<Error>>
After a connection is established, a handshake is completed by sending hello,
synctracker! and receiving hello, demo! as a response.
After this we listen with update() for further changes.
/// Read from the stream and process commands until the server runs out of
/// things to send.
///
/// Returns an Ok(true) if there should be a redraw.
pub fn update(&mut self, mut device: &mut SyncDevice) -> Result<bool, Box<Error>>
This runs a loop until the server runs out of things to send. The first byte is the instruction type, the rest will be the description of its data.
let mut is_sending = true;
while is_sending {
match self.stream.read(&mut cmd_buf) {
// ...
// interpret the received instuction byte
match code_to_cmd(cmd_buf[0]) {
NOOP => info!("Received: CMD NOOP, byte {}", cmd_buf[0]),
SetKey => self.handle_set_key_cmd(&mut device)?,
DeleteKey => self.handle_del_key_cmd(&mut device)?,
// ...
}
// ...
}
}
The rest of the code is implementing the handler functions.
Handling pause state for example:
pub fn handle_pause_cmd(&mut self, device: &mut SyncDevice) -> Result<(), Box<Error>> {
info!("Received: CMD Pause");
self.stream.set_nonblocking(false)?;
// get one byte, value 1 means paused
let mut buf = [0; 1];
self.stream.read_exact(&mut buf)?;
self.stream.set_nonblocking(true)?;
device.is_paused = { buf[0] == 1 };
info!("bytes: {:?}", buf);
info!("is_paused: {:?}", device.is_paused);
Ok(())
}
Onward to the sync lib!